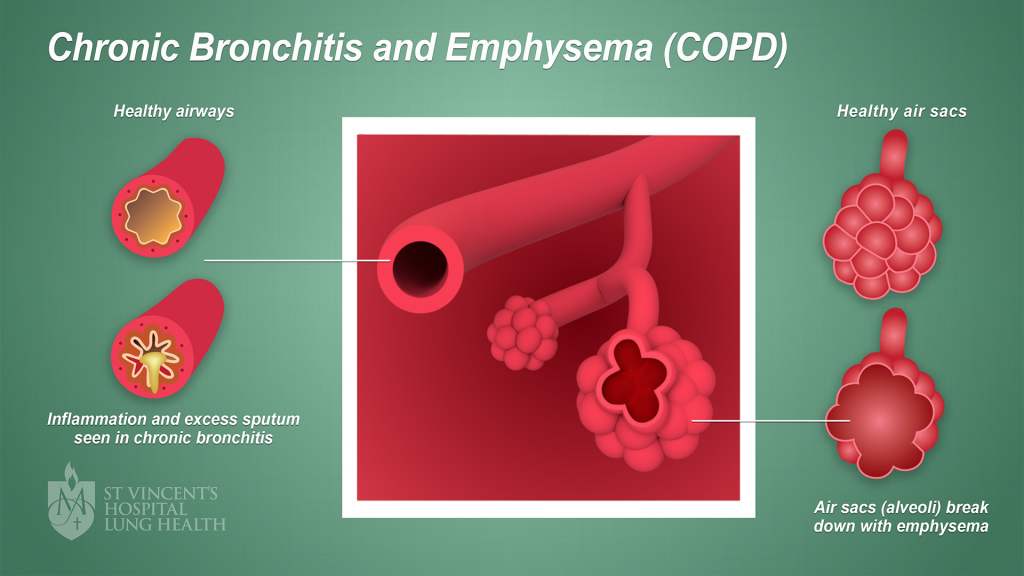
COPD stands for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. COPD refers to two types of lung disease:
- Chronic bronchitis – when the airways (the tubes that carry air into and out of your lungs) become partly blocked from swelling or mucus and you cough up phlegm
- Emphysema – when the air sacs which exchange gases at the end of your airways become damaged and enlarged, making it difficult to breathe.
When you have COPD, your airways become swollen and sometimes they get clogged with mucus. You can’t get enough fresh oxygen with each breath. You also find it difficult to push out the air.
Smoking is the most common cause of COPD. But, non-smokers can also get COPD. People who have been exposed to dusts can get COPD from dust inhalation. Second-hand smoke, also called passive smoking, is also a risk factor for COPD.
Other causes of COPD are:
Asthma – asthma that is not well controlled over a long period of time can lead to COPD
Infections – a disease called tuberculosis can lead to COPD
Pollution and fumes – including air pollution or breathing in chemical fumes, dusts or toxic substances.
In rare cases, people with COPD can have faults in their genes (the instruction manuals for how your body develops and works). These faults include a disease called “alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency” or AAT deficiency. People with AAT deficiency don’t have enough of a protein needed to protect their lungs from damage.
Leave a Reply